Mars has captivated the human imagination for centuries, and each new mission to the Red Planet expands our understanding of its mysteries. With recent discoveries about its surface, subsurface features, and atmospheric conditions, we are beginning to see Mars in a new light. From surprising subsurface ice patterns to the resilience of the Martian helicopter Ingenuity, these revelations provide insight into Mars’s complex geology, potential for past water flow, and future suitability for exploration and possibly even habitation.
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s Surprising Discoveries: A Glimpse at Martian Ice Patterns
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) has provided valuable data over the years, but one of its most recent discoveries has sparked significant interest. A fascinating image captured by MRO reveals intricate line patterns on the Martian surface, resembling ancient geoglyphs. These formations, believed to be influenced by the subtle movements of surface ice, suggest that ice deposits may be more widespread on Mars than previously thought. Found outside the polar regions, these patterns imply that Mars may harbor hidden ice beneath its surface across vast areas, challenging prior assumptions about the concentration of Martian ice.
Curiosity Rover’s Time-Lapse Photography: Revealing Martian Environmental Conditions
The Curiosity rover has been tirelessly exploring the Martian surface, capturing breathtaking time-lapse images that document the planet’s daily environment. These visuals provide rare glimpses into Martian weather patterns and atmospheric changes, showing shifts in shadow, dust movement, and the effects of cosmic rays. Despite the challenges of solar conjunctions—periods when communication with Earth is cut off—the rover continues to operate, revealing a dynamic and often harsh Martian landscape that poses both challenges and insights for future missions.
Exploring Martian Ice Beyond the Poles: An Unexpected Discovery
One of the standout revelations from Mars exploration is the presence of surface ice formations far from the polar regions. This discovery reshapes our understanding of how and where water may be stored on Mars. The presence of ice closer to the planet’s warmer regions raises questions about potential water availability for future missions, as well as the likelihood that Mars once held enough water to support a more diverse climate and perhaps even microbial life.
Subsurface Water Reservoirs in Medusae Fossae: Evidence of Hidden Ice
One of Mars’s most enigmatic regions, Medusae Fossae, has long intrigued scientists due to its unusual formations. Once believed to be shaped by volcanic activity, radar surveys now suggest the presence of vast underground water ice reservoirs, a groundbreaking discovery with significant implications. These findings imply that water may be stored in these reservoirs, potentially explaining Mars’s loss of surface water billions of years ago. For future missions, these hidden water sources could be key to supporting human exploration or colonization efforts on Mars.
The Ancient Waterways of Mars: River Valleys and Their Historical Significance
Mars’s river valleys, winding channels that reveal the presence of ancient flowing water, offer a window into the planet’s past. Through crater dating techniques, scientists have discovered that these valleys formed during multiple episodes of water flow, spanning hundreds of millions of years. This periodic water activity, likely caused by variations in Mars’s orbit and tilt, suggests that Mars may have experienced cycles of arid and wet periods, dramatically impacting its surface and potentially supporting conditions suitable for life.
Orbital Variations and Water Flow Cycles on Mars
The Martian landscape bears evidence of ancient water flows, pointing to periods when Mars was warmer and wetter. These shifts in climate appear to have been influenced by Mars’s orbital variations, or changes in its tilt and orbit around the sun, leading to cyclical warming and cooling. These periodic climate changes, spanning millions of years, indicate that Mars may have been a much more hospitable environment in the past than it is today, providing intriguing clues about its potential to support life.
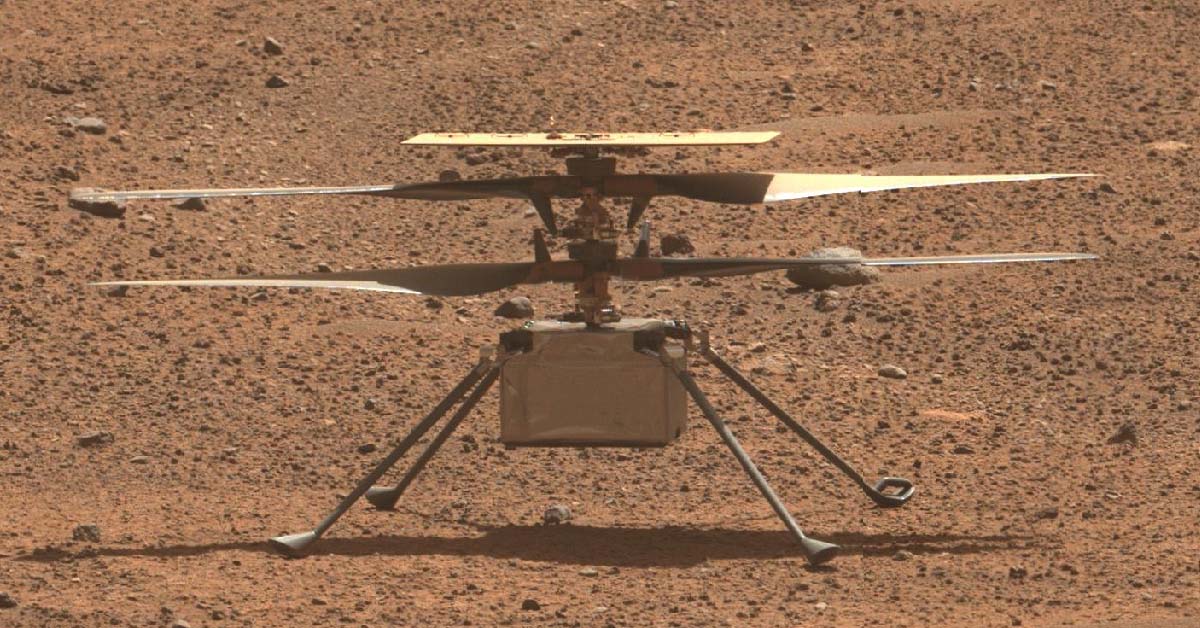
The Resilient Journey of Ingenuity: Mars’s First Helicopter
The Mars helicopter, Ingenuity, was initially designed for a short technology demonstration, yet it has exceeded expectations by flying over 70 times, collecting critical data and setting records along the way. Ingenuity’s groundbreaking journey showcases its durability and the immense potential of aerial exploration on Mars, inspiring scientists and enthusiasts alike. Its journey is a testament to engineering excellence, marking a milestone in space exploration and expanding our toolkit for planetary exploration.
Technical Triumphs and Challenges of Ingenuity’s Extended Mission
Ingenuity’s prolonged mission was not without challenges. Technical issues, including communication disruptions and flight errors, have tested the helicopter’s resilience and durability. Each issue presented new learning opportunities for scientists and engineers, who continuously adapted Ingenuity’s mission to extend its lifespan. These experiences have provided valuable insights for the development of future aerial vehicles designed for Mars and other planetary environments.
Damage to Ingenuity’s Rotor Blades: The Final Chapter of a Historic Mission
After an extraordinary run, Ingenuity’s mission reached its end following damage to one of its rotor blades. The 72nd flight showed images of the missing section, possibly caused by an unexpected landing or mechanical issue. Although Ingenuity’s journey has concluded, its achievements have left a lasting legacy, setting a foundation for future aerial missions on Mars and inspiring new designs that will expand our capabilities on other worlds.
Ingenuity’s Legacy and Influence on Future Aerial Missions to Other Planets
The knowledge gained from Ingenuity’s flights will inform future projects, including NASA’s planned Dragonfly mission to Titan, Saturn’s largest moon. By learning from Ingenuity’s successes and challenges, engineers are refining designs for aerial vehicles capable of exploring other planetary bodies. These advancements promise to revolutionize planetary exploration, enabling more efficient and flexible data collection on Mars and beyond.
Challenges in Sample Return Missions: Perseverance and the Cost of Bringing Mars Home
A potential sample return mission, which would retrieve Martian rock and soil samples collected by the Perseverance rover, promises groundbreaking scientific discoveries. However, the mission faces significant financial and logistical hurdles, as feasibility studies raise concerns about its high cost. Determining how to safely and affordably bring samples from Mars back to Earth remains a complex challenge for space agencies and one of the next big steps in Mars exploration.
The Next Frontier: Insights and Plans for Future Mars Missions
The recent discoveries on Mars have paved the way for more ambitious exploration goals. Future missions aim to further investigate Mars’s potential for life, study its climate history, and understand its geological evolution. Plans include sending more rovers, conducting sample return missions, and even preparing for the possibility of human exploration. Each mission builds upon the knowledge gained from past discoveries, bringing humanity closer to understanding the Red Planet’s mysteries.
Human Exploration and Colonization: How Recent Discoveries Shape the Dream of Living on Mars
The findings of subsurface ice reservoirs, evidence of past water flow, and the success of robotic exploration raise the possibility of Mars as a future home for humans. Understanding Martian resources, like ice that could potentially be used for water, oxygen, and even rocket fuel, is essential for the feasibility of long-term human missions. As technology advances and our knowledge of Mars grows, the dream of establishing a human presence on the Red Planet inches closer to reality.
Conclusion: Mars Exploration as Humanity’s Journey of Discovery and Innovation
The continued exploration of Mars exemplifies humanity’s drive to push boundaries and seek answers. From Ingenuity’s flights to the discovery of ancient water systems, each finding reveals a new piece of Mars’s complex story. As we reflect on these achievements, we are reminded of the spirit of curiosity, perseverance, and innovation that drives space exploration. With every mission, we uncover new possibilities for Mars and bring the universe a little closer to home.
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What recent discoveries have been made about ice on Mars?
Recent radar surveys suggest the presence of subsurface ice reservoirs outside of Mars’s polar regions, hinting at more widespread water deposits than previously thought. - 2. How has the Mars helicopter Ingenuity impacted Mars exploration?
Ingenuity has exceeded expectations, completing over 70 flights and demonstrating the potential of aerial exploration on Mars, which will influence future missions. - 3. Why is the Medusae Fossae region significant?
Medusae Fossae is thought to contain underground ice reservoirs, potentially solving the mystery of where Mars’s ancient water went and offering resources for future missions. - 4. Could Mars have supported life in the past?
Evidence of past water flow suggests Mars may have been warmer and wetter, raising the possibility that it could have supported microbial life. - 5. What is the goal of a sample return mission from Mars?
A sample return mission aims to bring Martian rock and soil samples to Earth, allowing scientists to analyze them for signs of past life and study Mars’s geological history. - 6. How might Mars exploration benefit future human colonization?
Discoveries like subsurface ice deposits could provide essential resources, making it feasible to support human life on Mars by supplying water, oxygen, and fuel.