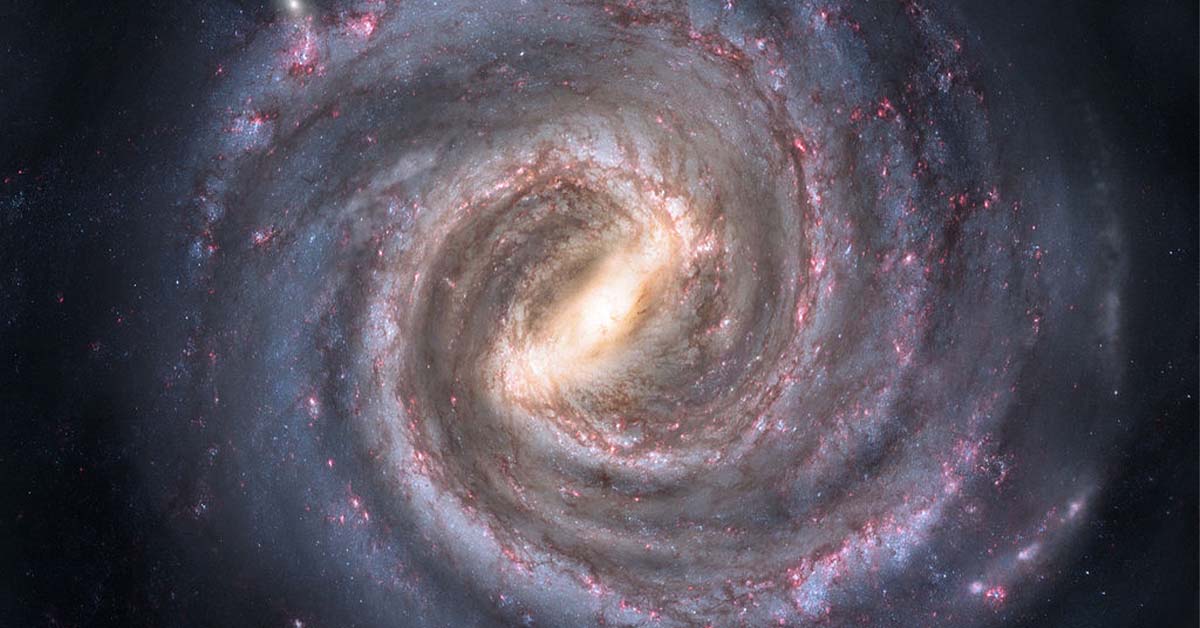
From ancient stargazers to modern astronomers, humanity has always been captivated by the mysteries of the universe. The Milky Way, our galaxy, is a dynamic, complex structure that has held the attention of scientists for centuries. Understanding its vastness, formation, and evolution is a central goal of astrophysics. Today, with the aid of advanced technology, astronomers are uncovering hidden secrets of our galaxy through projects like the Variables in the Via Lactea (VVV) survey.
The Milky Way Galaxy: A Cosmic Enigma
The Milky Way galaxy is more than just the collection of stars we see on a clear night; it is a vast structure containing billions of stars, interstellar dust, and mysterious dark matter. The galaxy’s bulge—the dense central region—contains an especially rich field for study, with complex star formations, dust clouds, and other celestial phenomena that offer insights into galactic dynamics. To unravel the mysteries of the Milky Way’s bulge, astronomers launched the VVV survey, a project dedicated to exploring the unique properties and hidden elements of our galaxy’s center.
The VVV Survey: Exploring the Variables in the Via Lactea
The VVV survey, short for Variables in the Via Lactea, is a groundbreaking astronomical endeavor focusing on the Milky Way’s core. This project, spanning nearly 14 years, is dedicated to monitoring the bulge region to detect changes in star brightness and capture other unusual celestial phenomena. By continuously scanning the central regions of the Milky Way, the VVV survey has revealed a range of stellar behaviors, including stars that seemingly disappeared and new variables that challenge our understanding of stellar evolution.
Harnessing Technology in Modern Astronomy
Astronomical exploration has advanced significantly over recent decades thanks to the power of technology, automation, and artificial intelligence. The VVV survey utilizes high-powered telescopes and data analysis tools that enable astronomers to monitor changes in thousands of stars simultaneously. AI and machine learning play an instrumental role in identifying patterns and anomalies in vast datasets, accelerating the rate of discovery and helping scientists track subtle variations across the Milky Way.
Unraveling Celestial Mysteries: The Discovery of “Missing Stars”
One of the VVV survey’s most compelling discoveries is the phenomenon of “missing stars.” These stars were visible in mid-20th-century observations but have since vanished, defying straightforward explanation. This unexpected observation challenges assumptions about stellar life cycles, raising intriguing questions about whether these stars might be undergoing extreme transformation, collapsing into black holes, or moving behind dense interstellar clouds.
Enigmatic Stars in the Milky Way: The Mystery of “Old Smokers”
Among the unique stellar phenomena uncovered by the VVV survey are the “Old Smokers,” stars with extremely high metallicity that exhibit dramatic fluctuations in brightness. The dust surrounding these stars, created by high metallic content, leads to sudden drops in luminosity and distinctive changes over time. Found mostly in the galaxy’s bulge, these stars deviate from the norm of red giants, shedding light on how metallicity and dust production shape the evolution of stars in unique ways.
The Role of Dust and Metallicity in Stellar Evolution
Dust plays a significant role in the brightness and appearance of stars, and high metallicity (abundance of heavy elements) intensifies dust production around certain stars, such as the “Old Smokers.” These dust clouds obscure the stars, impacting their brightness and creating fluctuations visible in observations. The abundance of heavy elements in the Milky Way’s bulge allows astronomers to study how metallicity influences stellar evolution, adding layers to our understanding of how stars form, live, and die.
Challenging Stellar Evolution Models: Insights from “Old Smokers”
The discovery of “Old Smokers” challenges existing models of stellar evolution, as these stars display behaviors and characteristics unaccounted for in traditional theories. Their fluctuating luminosity and high metallicity suggest that there are additional, complex processes at play in stellar aging, particularly in regions of the galaxy with abundant heavy elements. Such findings encourage astronomers to refine stellar models, considering new factors that could alter the lifecycle of stars in the Milky Way’s central regions.
Nova Events: Thermonuclear Explosions of White Dwarfs
The VVV survey has also documented numerous nova events—thermonuclear explosions occurring on the surfaces of white dwarf stars in binary systems. These events, marked by a sudden increase in brightness, provide essential information about stellar activity and evolution. Although novae are relatively common, each explosion is unique, adding to our understanding of stellar mass accumulation and the complex dynamics of binary star systems.
Cataclysmic Stellar Events and Galactic Dynamics
Nova events offer more than just dramatic visuals; they are critical to understanding the dynamics of the Milky Way. These explosions release energy, material, and light into the surrounding space, impacting nearby interstellar matter. By studying nova events, astronomers gain insight into the life cycles of binary stars, as well as the broader impact of these explosive events on galactic evolution.
Technological Advances in the VVV Survey and Astronomy
The success of the VVV survey highlights the importance of technological advancements in astronomy. Modern telescopes equipped with high-resolution imaging capabilities allow researchers to gather comprehensive data on the Milky Way’s core. Coupled with automated data processing, these tools enable scientists to explore vast sections of the galaxy efficiently, uncovering stellar events and phenomena that would be impossible to observe with manual techniques.
Automation and Artificial Intelligence in Space Exploration
Artificial intelligence has become an invaluable tool in analyzing the vast datasets generated by surveys like the VVV. Machine learning algorithms sift through data, identifying anomalies and tracking subtle changes in brightness or position, which are critical in studying variables and novae. The use of AI in astronomy accelerates discovery, enabling astronomers to uncover stellar phenomena that could otherwise go unnoticed.
The Importance of the VVV Survey in Galactic Mapping
Mapping the Milky Way’s bulge is a monumental task, but the VVV survey’s systematic approach to monitoring the bulge area provides valuable insights into this dense region. The survey not only contributes to galactic mapping but also enhances our understanding of how stars interact with the dense interstellar medium. With each discovery, astronomers gain a clearer view of the Milky Way’s structural complexity and its dynamic processes.
Future Prospects for the VVV Survey and Beyond
The VVV survey is only the beginning of what is possible with modern astronomy. Future missions will expand upon its discoveries, exploring different regions of the Milky Way and beyond. By combining observations from multiple wavelengths and further incorporating AI-driven analysis, astronomers hope to delve even deeper into the unknown, uncovering more details about the galaxy’s core and the lifecycle of stars.
Conclusion: A Journey of Discovery in the Milky Way Galaxy
The VVV survey exemplifies humanity’s quest to explore the cosmos and unlock the secrets of the Milky Way. Through technological innovation and advanced research methods, astronomers are uncovering an array of celestial phenomena, from missing stars to enigmatic “Old Smokers” and nova explosions. Each discovery brings us closer to understanding the universe’s complexities and the mysteries of our galaxy. As we continue our journey into the cosmos, the Milky Way promises endless fascination and boundless mysteries to explore.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the VVV survey?
The Variables in the Via Lactea (VVV) survey is an astronomical project focused on the Milky Way’s bulge, aiming to detect changes in star brightness and discover new celestial phenomena.
2. What are “Old Smokers” in astronomy?
“Old Smokers” are stars with high metallicity that produce dense dust clouds, causing dramatic changes in their brightness. They are primarily located in the Milky Way’s bulge.
3. Why are nova events important in astronomy?
Novae are explosive events on white dwarf stars that provide insights into stellar evolution, binary star dynamics, and galactic energy distribution.
4. How does AI help in astronomical surveys like the VVV?
AI assists by analyzing vast datasets, identifying anomalies, and tracking changes in star brightness, accelerating discoveries that would be challenging to achieve manually.
5. How does the VVV survey contribute to galactic mapping?
The VVV survey’s focus on the Milky Way’s bulge offers a detailed map of this dense region, helping scientists understand the galaxy’s structure and dynamic processes.
6. What’s next for research after the VVV survey?
Future research will expand to other parts of the Milky Way, using advanced telescopes and AI to explore more of the galaxy and its diverse celestial phenomena.