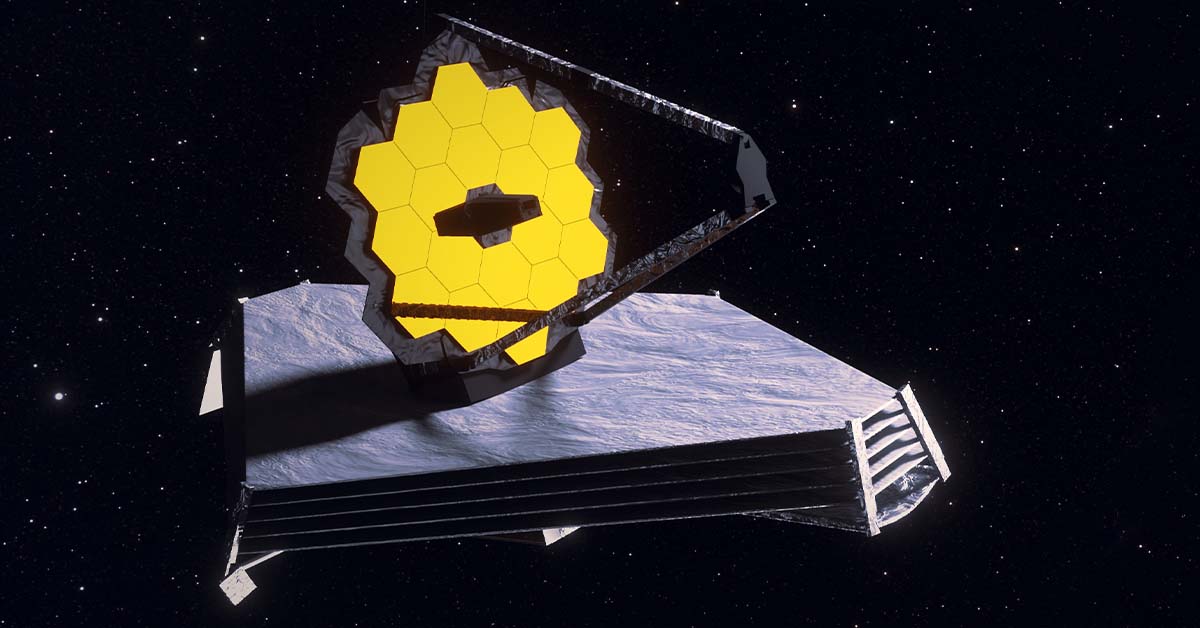
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) represents one of humanity’s greatest achievements in the exploration of the cosmos. A marvel of engineering and vision, JWST stands as a testament to our unyielding curiosity and desire to understand the universe’s deepest mysteries. Launched in 2021, JWST has already opened new horizons, unveiling cosmic phenomena that were previously out of reach. This groundbreaking telescope promises to reshape our understanding of the universe, from the birth of stars and galaxies to the secrets hidden in the distant reaches of space.
A New Era in Astronomy: The JWST’s Capabilities
The James Webb Space Telescope is equipped with advanced technology that distinguishes it from previous telescopes. Its primary mirror, composed of 18 hexagonal segments, spans over 6.5 meters, giving it the power to capture incredibly faint light from galaxies billions of light-years away. Additionally, JWST’s infrared capabilities allow it to peer through cosmic dust clouds that obscured Hubble’s view, revealing new levels of detail in stellar nurseries, planetary systems, and distant galaxies.
Unveiling the Cosmic Treasures
In its first months of operation, JWST has already captured astonishing images of galaxies, stars, and other cosmic structures across the universe. These images showcase the rich diversity of galactic forms and phenomena that populate the cosmos. Some of the telescope’s most significant discoveries include galaxies in various stages of formation, revealing structures and interactions that challenge existing theories. JWST’s observations suggest that these ancient galaxies, some dating back over 13 billion years, played a critical role in shaping the universe’s development.
Building on Hubble’s Legacy
The Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990, fundamentally changed our view of the cosmos. Its iconic images, including the Hubble Ultra Deep Field, provided glimpses into the universe’s earliest moments and laid the groundwork for modern astronomy. While Hubble focused primarily on visible and ultraviolet light, JWST’s infrared capabilities take Hubble’s achievements even further. JWST can see deeper into the cosmos, offering a clearer view of galaxies, stars, and planetary systems that were once hidden. With this new perspective, JWST builds on Hubble’s legacy, pushing the boundaries of cosmic exploration to new heights.
Exploring the Oldest Galaxies
One of JWST’s primary goals is to explore the universe’s oldest galaxies. These ancient structures, formed shortly after the Big Bang, contain valuable clues about the cosmos’s early conditions. Using its powerful instruments, JWST has already detected galaxies that appear as elongated shapes—structures that astronomers describe as “surfboard” galaxies. These unique shapes may represent stages of galaxy formation previously unknown, providing a window into the processes that governed the early universe.
Studying Galactic Formation and Evolution
JWST’s observations have transformed our understanding of how galaxies form and evolve. By studying ancient galaxies at varying distances, scientists can map how these structures changed over billions of years. The presence of supermassive black holes at the center of many ancient galaxies adds to the intrigue, as it suggests that black holes may have influenced galaxy formation from the beginning. JWST’s ability to capture these details in ancient galaxies has led astronomers to rethink established theories of cosmic evolution.
Galactic Quenching: The Role of Black Holes
One of the most fascinating phenomena JWST has observed is galactic quenching—the process by which star formation slows down or halts entirely within certain galaxies. This effect appears to be connected to the activities of supermassive black holes, whose gravitational pull and energy emissions can disrupt the gas needed for star formation. By observing these interactions in detail, JWST has shed light on the delicate balance between black hole activity and galactic evolution. These findings underscore the role that supermassive black holes play in shaping the fate of entire galaxies.
Black Hole Mass Patterns Across the Universe
In addition to galactic quenching, JWST has also revealed intriguing patterns in black hole mass distribution across cosmic scales. Observing the mass and activity levels of black holes in galaxies at different stages of evolution provides valuable data on how black holes grow and change over time. This information is essential for developing a comprehensive understanding of the complex interactions between black holes and galaxies in shaping cosmic history.
Cosmic Web and Galaxy Clusters
The universe’s structure, often referred to as the cosmic web, consists of galaxies and clusters interconnected by vast filaments of dark matter. JWST’s advanced observational capabilities allow it to detect and map this intricate web with unprecedented clarity, offering insights into the large-scale organization of the universe. By studying galaxy clusters and the cosmic web, JWST enables scientists to understand the forces and patterns governing galaxy distribution and formation.
Probing Deep Space: Farthest-Known Quiescent Galaxies
Among JWST’s many discoveries are quiescent galaxies, which have stopped forming stars and represent a later stage in galactic evolution. These galaxies offer a snapshot of cosmic maturity, showcasing how galaxies age and evolve. By examining these quiescent galaxies, scientists gain insights into the universe’s lifecycle and the processes that cause galaxies to “settle down” over time.
Uncovering Star Formation in the Distant Universe
Star formation is a dynamic process that varies across different cosmic epochs. JWST has the power to observe regions where stars are actively forming, providing a glimpse into the lifecycle of stars across vast time spans. These observations are crucial for understanding how elements essential for life, such as carbon and oxygen, are produced and distributed throughout the universe.
Exploring Exoplanets and Planetary Systems
In addition to studying distant galaxies, JWST is equipped to investigate exoplanets and their atmospheres. By analyzing the light passing through exoplanet atmospheres, JWST can detect the presence of various gases, potentially identifying habitable conditions or even signs of life. These capabilities have transformed JWST into a powerful tool for the search for extraterrestrial life, extending humanity’s quest to understand our place in the cosmos.
Peering into Our Own Solar System
While JWST’s primary mission focuses on distant galaxies, it is also contributing valuable data on our solar system. Observing planets, moons, and other bodies within our solar neighborhood allows scientists to refine models of planetary evolution and atmospheric dynamics. For example, JWST’s observations of outer planets and their moons offer new perspectives on planetary weather systems, chemical compositions, and potential for supporting life.
Expanding the Frontiers of Human Knowledge
The James Webb Space Telescope embodies the pinnacle of human ingenuity and determination. With each new observation, JWST expands the limits of our understanding, challenging scientists to rethink long-standing assumptions about the universe’s origins and structure. JWST’s findings inspire not only the scientific community but also the broader public, reminding us of the boundless potential of discovery and exploration.
Conclusion: A Universe of Possibilities
In conclusion, the James Webb Space Telescope is more than just a scientific instrument; it is a symbol of humanity’s quest for knowledge and exploration. With its advanced technology and unprecedented reach, JWST has already transformed our understanding of the cosmos, unveiling hidden aspects of the universe and providing answers to questions we had never thought to ask. As we continue to explore with JWST, we celebrate