Ancient artifacts serve as portals to the past, helping historians and scientists piece together the story of human civilization. Among these artifacts, clay tablets from Mesopotamia and other regions stand out as enduring records of early human activity. Now, through a newly developed dating technique based on the analysis of Earth’s magnetic field, scientists are able to not only date these ancient objects with increased accuracy but also gain insights into a magnetic anomaly that occurred thousands of years ago. This discovery represents an interdisciplinary milestone, connecting archaeology with geophysics and expanding our understanding of Earth’s hidden magnetic history.
Clay Tablets: Portals to the Past
Significance in Historical Research
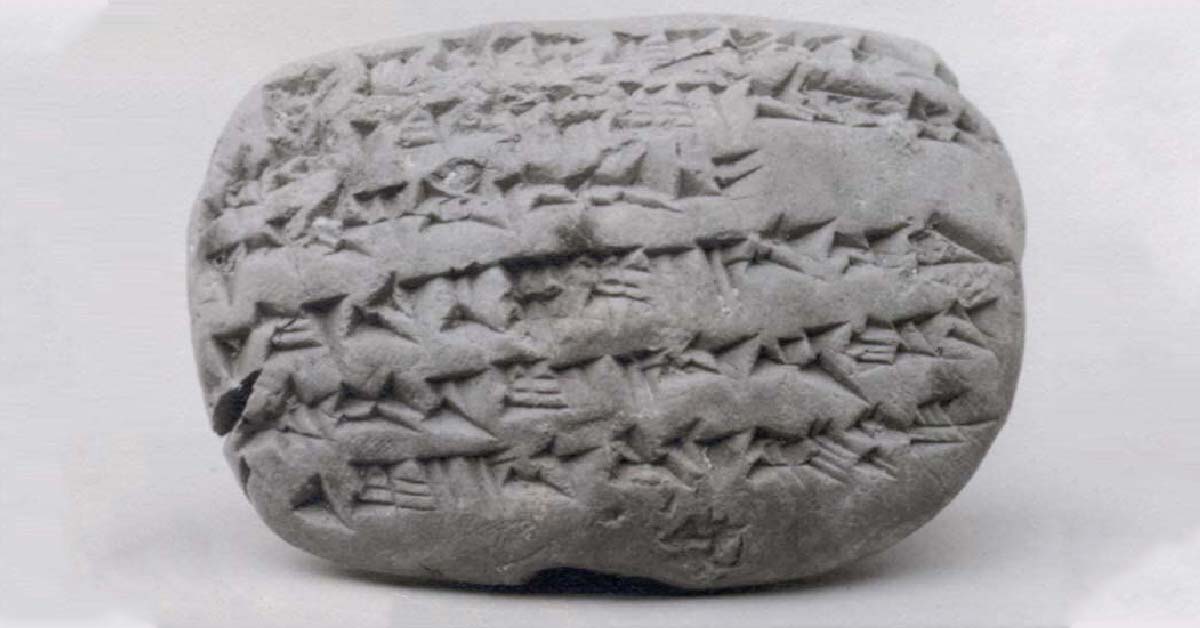
Clay tablets are invaluable for researchers, capturing the daily transactions, myths, laws, and social exchanges of ancient civilizations. Predominantly found in the Middle East, these tablets offer a rare look into the cultural and economic lives of people from over 4,000 years ago. Many of these tablets, used for everything from tracking grain supplies to recording epic stories, are among the earliest known records, making them indispensable to archaeologists and historians.
Challenges in Traditional Dating Methods
Traditionally, dating artifacts requires organic material for carbon dating. However, clay tablets typically lack organic components, presenting a challenge for accurate dating. This new technique of magnetic dating leverages the iron oxides within the clay, which can capture and retain information about Earth’s magnetic field at the time of the tablet’s creation, allowing for precise dating even in the absence of organic matter.
Exploring Earth’s Magnetic Anomalies
Magnetic Anomalies Across Time
Earth’s magnetic field has fluctuated over millions of years, creating periodic anomalies that influence the entire planet. These anomalies occur when changes in Earth’s molten core impact the magnetic field’s strength and orientation. By studying magnetic anomalies recorded in ancient materials, scientists can reconstruct a timeline of these changes, offering insights into shifts in the geomagnetic field that affected past climates and possibly even human civilization.
Modern Comparison: The South Atlantic Anomaly
The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA) is a current magnetic anomaly characterized by a weakened magnetic field over parts of the Atlantic Ocean. This anomaly poses a risk to modern satellites, spacecraft, and even aircraft, which are vulnerable to increased cosmic radiation in regions where Earth’s magnetic shield is weakened. The SAA offers a contemporary comparison to ancient magnetic anomalies, helping scientists understand the potential impact of past events on ancient societies.
Magnetic Dating: Unlocking Ancient Secrets
The Role of Iron Oxides in Clay
Iron oxides, naturally present in clay, align with Earth’s magnetic field as the clay hardens, effectively recording a snapshot of the magnetic field’s strength and orientation. Researchers realized they could analyze these iron oxide orientations to deduce the approximate time of the artifact’s creation, using Earth’s magnetic history as a dating reference.
Dating Artifacts Through Magnetic Field Variations
In a groundbreaking study, scientists used magnetic dating on clay tablets to identify a geomagnetic anomaly occurring between 1050 BC and 550 BC. This technique, known as archaeomagnetic dating, is based on observing the variations in the magnetic field strength and direction over time. The 500-year-long anomaly revealed by the tablets may have been a global phenomenon, with implications for understanding not only Earth’s history but also the factors driving magnetic fluctuations over time.
Implications Beyond Archaeology
Understanding Earth’s Magnetic History
The ability to date artifacts through magnetic analysis has profound implications for reconstructing Earth’s magnetic history. By mapping ancient magnetic field anomalies, scientists are building a chronological record of magnetic fluctuations that span thousands of years. These fluctuations are essential to understanding the ongoing behavior of Earth’s magnetic field and may shed light on how the planet’s core dynamics impact its magnetic shielding.
Impact on Solar Studies and Modern Technology
The study of Earth’s magnetic history is crucial for understanding solar interactions with our planet. Magnetic anomalies make Earth more vulnerable to solar storms, which can disrupt technology and even threaten electrical infrastructure. By learning from past anomalies, scientists hope to improve our preparedness for future solar events and better understand the complex interactions between Earth’s magnetic field and solar activity.
Interdisciplinary Significance
Influence on Magnetosphere Research
Research into Earth’s magnetic past is invaluable to magnetosphere studies, which examine how Earth’s magnetic field protects us from cosmic radiation and solar winds. Understanding the frequency and causes of magnetic anomalies over millennia helps scientists predict future fluctuations and prepare for potential disruptions. This new knowledge could play a pivotal role in the development of space technologies and planetary defense systems.
Broad Implications for Planetary Science
Studying magnetic anomalies on Earth also has implications for planetary science. By analyzing magnetic records from other celestial bodies, scientists may be able to uncover similar magnetic histories, offering clues about planetary formation and evolution. Insights from Earth’s anomalies could inform research on planets like Mars, where magnetic field loss has dramatically impacted the planet’s atmosphere and surface conditions.
Towards a Deeper Understanding
Future Research Directions
While the new magnetic dating technique has revealed significant insights, many questions remain. Researchers aim to refine these dating methods further, applying them to a broader range of artifacts and regions. Future studies may explore the relationship between magnetic anomalies and climate changes, volcanic activity, or even patterns in ancient human migration.
Refining Magnetic Dating Techniques
As magnetic dating continues to evolve, scientists are working to enhance its precision. By combining magnetic data with other dating methods, they hope to create more accurate timelines of past events. These advancements in dating will allow researchers to verify historical accounts, map ancient environmental conditions, and provide a clearer picture of Earth’s magnetic field changes over time.
Conclusion: Bridging Past and Present
The study of ancient artifacts through magnetic dating represents a remarkable convergence of archaeology and geophysics, offering new ways to explore our planet’s history. By unlocking the magnetic records embedded in clay tablets, scientists have developed a technique that not only aids in dating ancient objects but also illuminates Earth’s magnetic history and its long-term impacts on civilization and technology.
As we deepen our understanding of Earth’s magnetic anomalies, we gain insights that are relevant for both the past and the future. This interdisciplinary research enhances our ability to comprehend and protect against modern magnetic fluctuations, bridging the gap between ancient history and contemporary scientific inquiry. Through continued exploration of ancient artifacts and their hidden magnetic signatures, we move closer to unraveling the mysteries of Earth’s magnetic past and the broader forces that shape our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q1: What is magnetic dating, and how does it work?
- Magnetic dating analyzes the alignment of iron oxides in artifacts like clay tablets, which record the direction and strength of Earth’s magnetic field at the time of creation. By comparing this data to known magnetic history, scientists can date the artifact.
- Q2: Why are clay tablets significant in archaeology?
- Clay tablets are among the oldest written records, providing detailed accounts of ancient civilizations’ laws, commerce, and culture. They are critical for understanding the history and development of early human societies.
- Q3: How does Earth’s magnetic field affect modern technology?
- Earth’s magnetic field protects us from cosmic radiation. When anomalies weaken this field, as seen in the South Atlantic Anomaly, it can disrupt satellites, aircraft, and even ground-based electrical systems.
- Q4: What did the study reveal about ancient magnetic anomalies?
- The study identified a magnetic anomaly between 1050 BC and 550 BC, indicating significant fluctuations in Earth’s magnetic field strength. This anomaly suggests a global phenomenon with potential impacts on past climates and environments.
- Q5: How might magnetic anomalies influence planetary science?
- Understanding Earth’s magnetic anomalies helps scientists study other planets, especially those without strong magnetic fields. Insights from Earth may inform our understanding of planetary atmospheres, climates, and potential for life on other worlds.
- Q6: What are the future implications of magnetic dating for archaeology?
- Magnetic dating may provide archaeologists with an additional tool to accurately date artifacts without relying on organic material, expanding the scope of historical research and enhancing our understanding of ancient cultures.